SLE
Selective Laser Etching to minimize tapering and surface chipping on transparent materials.
Release constraints on structure size and material thickness thanks to combining technology femtosecond lasers with chemical etching. Through local modifications, this process enables the direct fabrication of true 3D micro-devices within transparent materials.
Selective Laser Etching (SLE) is a sophisticated fabrication technique that facilitates the formation of intricate 3D microstructures in transparent materials, while reducing tapering and surface chipping. By integrating femtosecond laser technology with chemical etching, SLE transcends traditional constraints on structural dimensions and material thickness, facilitating high-precision and superior-quality machining.
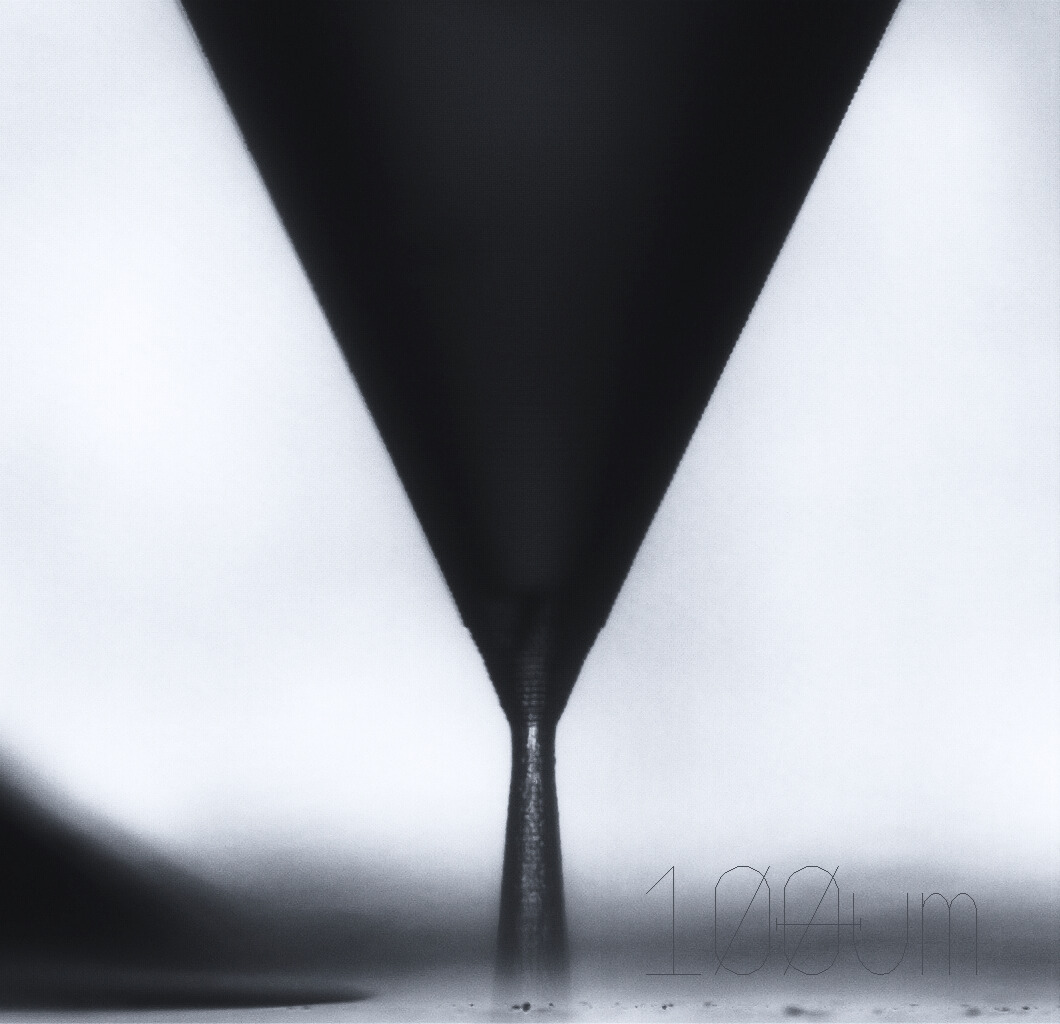
A significant benefit of SLE is its capacity to directly create complex internal and external structures in glass and other transparent materials without the need for masks or mechanical processing. This process facilitates the fabrication of functional microdevices, including microfluidic channels, capillary nozzles, lenses, and other high-precision components utilized in biomedical, optical, and MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) applications.
Moreover, SLE facilitates freeform 3D structuring, enabling the fabrication of both flat and irregularly shaped elements with minimal post-processing. SLE is a transformative technology for industries requiring specialized, miniaturized, and intricate components, due to its capacity for superior edge quality, high structural integrity, and sub-micron precision.
HOW DOES IT WORK
Femtosecond lasers have the capability to selectively induce local modifications within transparent materials, owing to their strong nonlinear absorption. These internal modifications lead to structural and chemical changes that can be specifically eliminated by immersing the samples in aqueous solutions of etchants such as hydrofluoric acid (HF) or potassium hydroxide (KOH).
FLEXIBILITY OF SHAPES
SLE technology can form various structures in glass, that includes:
-
Flat or free-shape 3D structures
-
Surface or internal channels
-
Microfluidic channels
-
Capillary nozzles
-
Lenses
-
Various micromechanics elements
-
many other...